It’s been clear for a while that mobile devices are the current market players, even more so that some experts have been counting on them to take over the PCs and Desktops in near future. But as with any emerging technology, developing and implementing mobile applications can pose a number of unique challenges.
Mobile applications, although have limited computing resources, are often built to be as agile and reliable as PC-based applications. In order to meet the challenge, mobile application testing has evolved as a separate stream of testing.
By missing the major user characterizations, mobile application lose the “gloss” within first couple of months and therefore, user retention period for mobile applications is very low, only around 10% users are found still using the same mobile application after six months of its download.
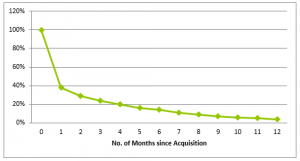 Mobile application user retention over period
Mobile application user retention over period
Many people have pointed fingers at many aspects and loop holes in Mobile App Testing, some of which are mentioned below.
- The major challenge in Mobile App Testing is the multiplicity of mobile devices with different capabilities, features and restrictions. Devices may have different technical capabilities such as amount of available memory, screen resolution, screen orientation and size of the display, network connectivity options, support for different standards and interfaces.
- Many mobile solutions involve a significant hardware element in addition to the PDA, such as scanners, mobile telephony, GPS and position based devices, telemetry, etc… These extra hardware elements place additional demands on the tester, particularly in terms of isolating a bug to hardware or software.
- Mobile applications are often intended to be used by people with no technical or IT background; such as meter readers, milkmen, insurance sales people; on devices that have small screens, and no or awkward keyboards. Good usability testing, carried out in conjunction with key users, in their own environment, is essential.
- There are multiple operating systems that are prevalent in the mobile space like Symbian, Android, iPhone OS, Windows, Linux, Blackberry OS, palm OS, Brew, etc. Each of the operating systems can have further versions for different types of devices which makes platform testing complex and further challenging
- Another challenge is that the developers need to focus on developing applications that are easy to use on a mobile and consume less power.
The Most important aspect that our analysis, development and testing teams often miss is that mobile application development takes a lot less time duration then mobile application testing, compared to the conventional model where application analysis & development takes more time precedence over testing. We therefore, deliberately tend to give less time for testing which might result in the application starting to lose out to competition over time. Due to this misunderstanding and thus improper testing strategy in mobile application; growing number of mobile applications are being taken off-app store every month, just in September 2011 alone following stats were witnessed
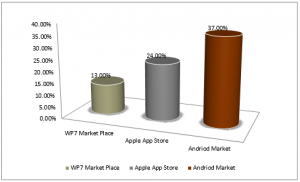 Percentage of applications taken off the stores
Percentage of applications taken off the stores
These trends show, that we can never use the same testing methodologies as we have been using on the conventional web and desktop applications, we have to devise a new strategy and methodology, which is going to take into account what actually is the mobile world, what it constitutes of and the adjustments it calls for in our conventional testing patterns and strategies.


